Understanding Invisible Advantages: Network Distance, Latency, and Their Application to the Solana Environment
Understanding Invisible Advantages: Network Distance, Latency, and Their Application to the Solana Environment
Network and internet speed are hard to see and even harder to visualize how to improve, so speculation tends to get ahead of facts. Still, the internet is a communications technology with clear fundamentals. All information travels as light through fiber inside cables. Performance is shaped by cable length and switches, and by the everyday reality of incidents, maintenance, and improvements happening somewhere on the network.
It may look complex because there are many participants and the overall scale is large, but the principles are surprisingly simple. There is no magic that enables instantaneous teleportation. Nothing violates the laws of physics. This is why making network distance work in your favor is the only strategy that is both repeatable and effective for getting faster.
The basic rule of the internet is simple: closer is faster
The shorter the fiber run and the fewer switch hops, the shorter the round trip time. Over longer distances, the number of waypoints increases and the path is more exposed to congestion and maintenance. Arrival times vary more. The closer you are, the smaller the variance and the higher the repeatability. You can understand this by travel intuition. Short trips tend to arrive roughly on schedule, while long trips fluctuate widely. Networks behave the same way. This is why the financial industry manages cable length down to centimeters and even prices distance as a resource. Reducing distance directly translates into results.
A commonly used indicator of network speed is bandwidth, described as 1 Gbps, 10 Gbps, or 25 Gbps. This is equivalent to the number of lanes on a road. More lanes allow more data to pass simultaneously and reduce congestion. Being close and having many lanes is the basic recipe for moving large volumes of data quickly.
Regaining an intuition for speed
When you think about networks, imagine you are driving a car. Your starting point is your server, and your destination is the target server. Nearby trips are simple and quick with lower risk of accidents and traffic jams. Long trips pass many intersections, highways, and tunnels, and congestion can appear anywhere along the route. Conditions are not the same every day, and the farther you travel, the higher the chance of encountering incidents. Bringing the destination closer is the shortest path to both the fastest and the most stable outcome.
Why distance has a price in finance
If you handle data from the New York Stock Exchange, it is intuitive to place your servers in New York. Going further, the ideal is to secure only a few centimeters of cable between your rack and the target server. This is a domain where significant premium pricing applies. Because the data source is fixed to a single location, the optimal choice is clear. Shortening cable length improves both speed and certainty, which is why rack position commands a premium. Closer is simply faster.
Solana’s reality and the path to winning
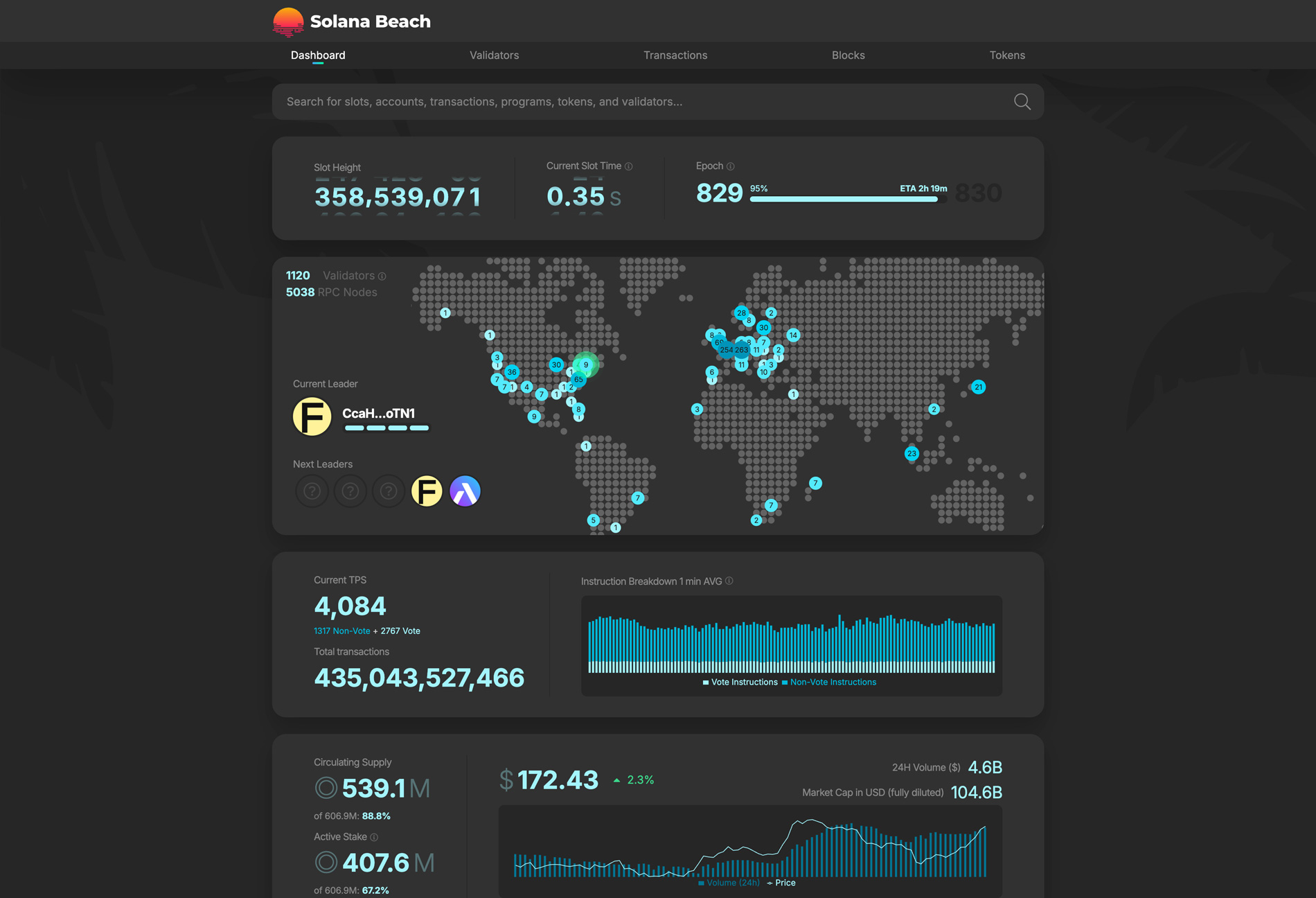
On Solana, the leader validator changes every slot and is responsible for transaction intake and block production. The data source therefore moves around the world moment by moment. At present, validators are concentrated in Frankfurt, which hosts roughly 20 to 27 percent. This geographic factor is one reason Frankfurt is so popular for Solana workloads.
Professionals aiming for the extreme do not stop there. They deploy resources across all major regions and process near the target leader slot. Even if you do not aim to cover everything, this reality defines how to compete. Start by understanding where validators are, decide where to place your resources, and identify your time windows of opportunity.
Here is the first and most practical step toward the fastest setup. When a Frankfurt validator is the leader, use servers inside the Frankfurt network. When a New York validator is the leader, use servers inside the New York network. Rigorously following this principle is a realistic strategy that reaches the minimum possible latency.
Application placement determines latency
Speed is not decided by server specs alone. Where your application lives is equally important. Monitoring what happens in Frankfurt from Tokyo is a disadvantage. Round trip delay accumulates and you are always reacting late. Prepare resources in each region, process locally where the data arrives, or bypass along the shortest path to the next local region. This raises both coverage and responsiveness. Returning to the core principle: connect to Frankfurt leaders from Frankfurt, and to New York leaders from New York. Start by doing this carefully.
ERPC provides options for optimal networks, server resources, and application placement based on these fundamentals.
We also offer APIs that make it easy to track constantly changing validator and leader information on Solana, providing comprehensive support across the platform.
Leader Slot API for handling instant “closeness” with data
Ordinarily, you would need to track the epoch position, estimate slot timing, extract leader candidates, reconcile with the cluster’s node list, run real ping measurements while accounting for geolocation errors, and persist and update results every epoch. This requires a sophisticated data platform.
To remove that burden, we already provide the Leader Slot Information API (getLeaderSlots API). With ERPC credits, you can query slot schedules, validator locations, and reference ping values. In practice, you can ask, “what is closest right now” or “at what times is Frankfurt close to the leader,” using the same workflow as standard Solana RPC.
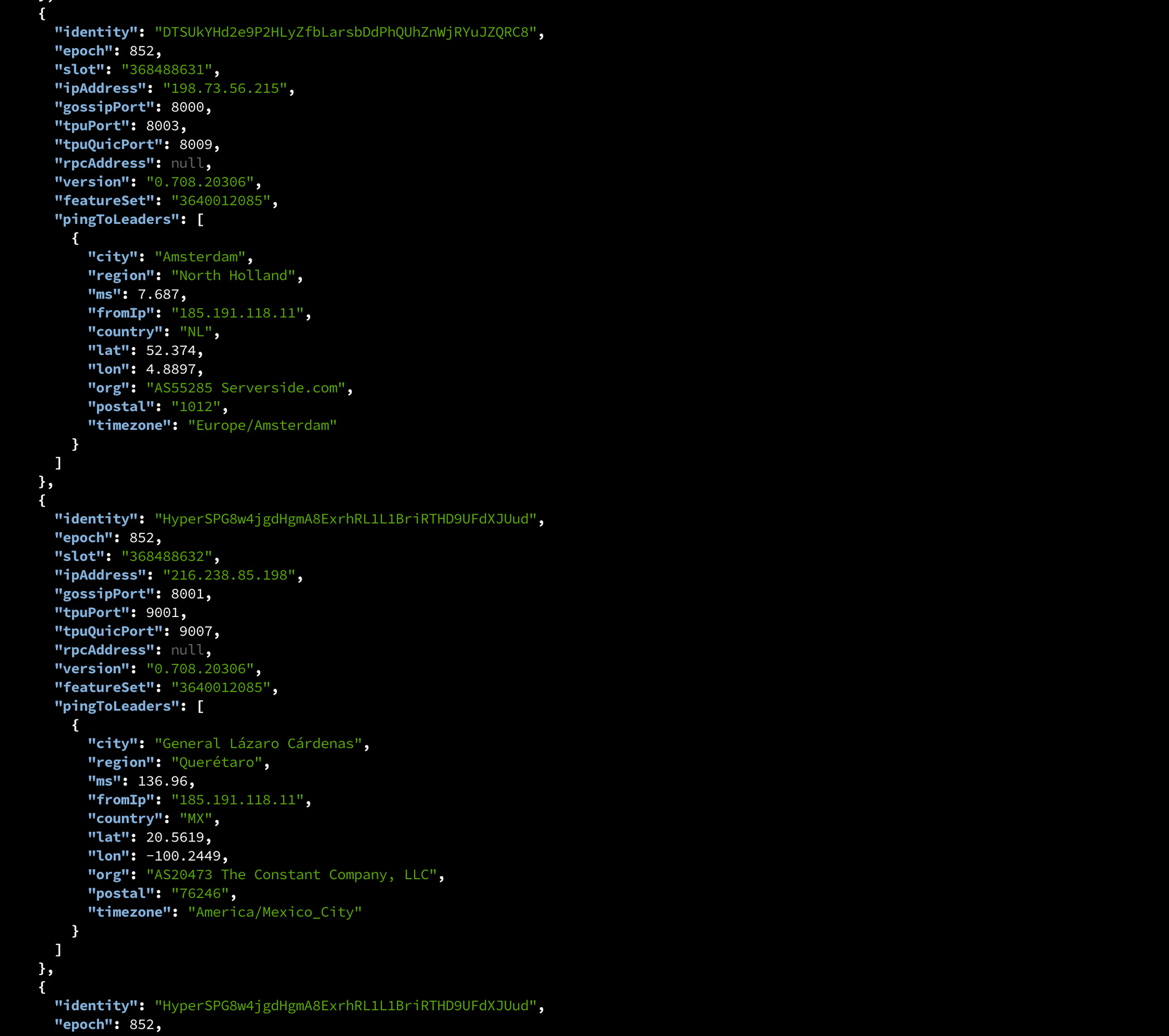
As a rule of thumb, when ping from your observation point exceeds 100 ms, a direct approach to that leader becomes less efficient. Intercontinental paths often exceed 100 ms. For example, instead of connecting from Frankfurt to a New York leader, using New York resources will be superior for both detection and sending. The getLeaderSlots API is designed to make this decision based on real latency.
Network distance does not always match the map
Even if two points look close in a straight line, they can be far apart on the network. Traffic flows through fiber, routers, and switches, so data does not necessarily take the shortest-looking route on a map. Within Europe, Frankfurt may look closer on the map, but depending on actual routes and congestion, Amsterdam often turns out to be faster.
To solve this, ERPC has upgraded all shared Solana endpoints. We introduced ping-based automatic routing in every region so that the system can automatically choose the shortest path based on your actual network distance.
Legacy routing based on IP geolocation often produced detours due to inaccuracies and stale records. In the new system, endpoints in each region automatically measure ping to allowlisted IPs and aggregate the results globally to decide the shortest path. This always selects the shortest path by measurement, and routing that depends on IP records alone has been completely retired.
Ping-based auto routing not only gives each user the fastest path, it also improves overall network efficiency. When everyone uses their own shortest path, long-haul load is reduced and global congestion eases. The result is a more stable response for Solana access worldwide.
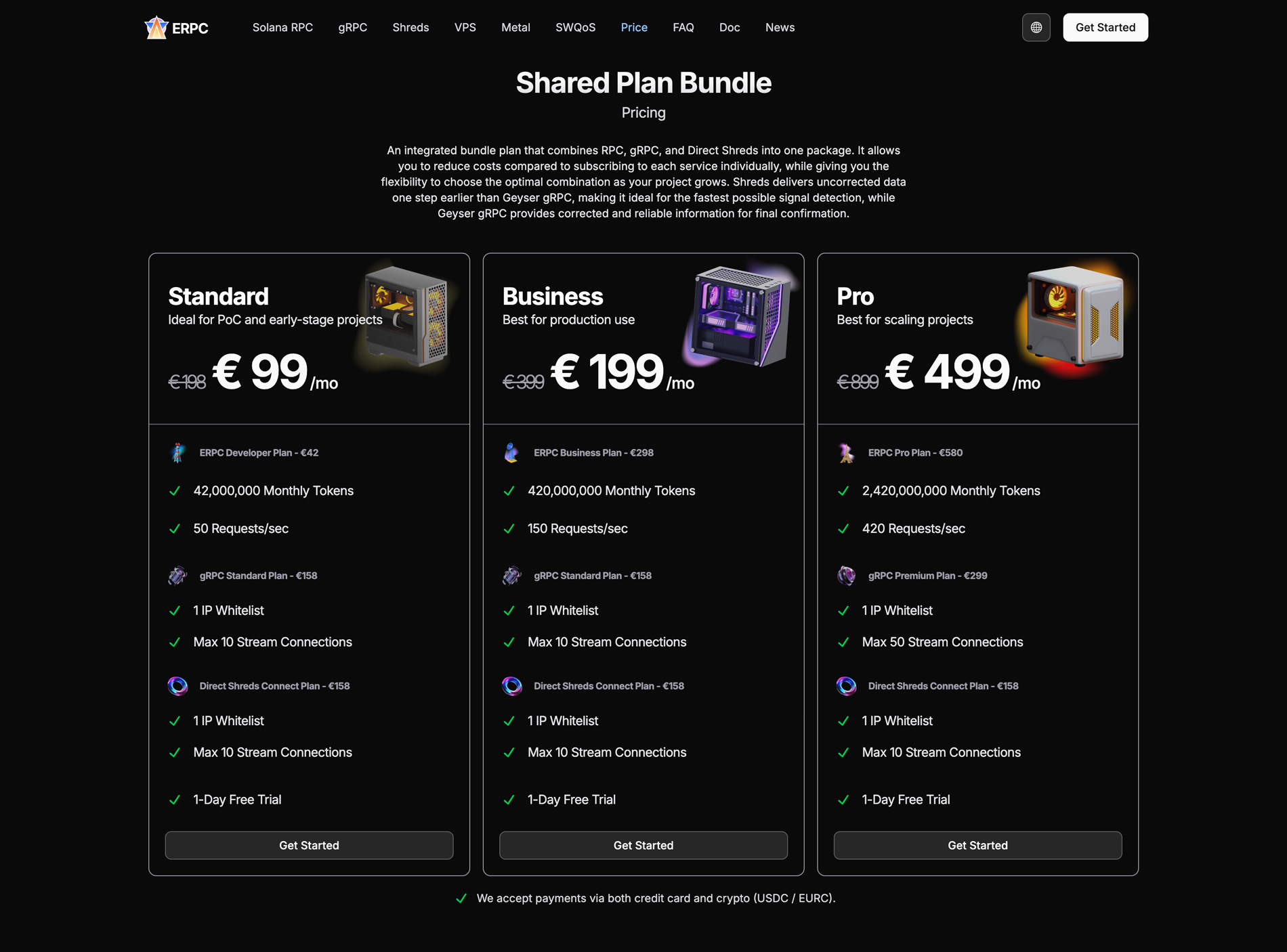
Solana RPC Bundle plan
Many developers start streaming on Solana with Geyser gRPC. It is easy to adopt because the data is already decoded, examples are plentiful, and the learning curve is low.
Professionals use the faster Shredstream. There is strong practical demand to keep current apps stable on gRPC while bringing in the benefits of faster Shreds in parallel. The Bundle addresses this need.
Until now, teams wanting to try a faster connection often struggled to take the first step due to environment setup and cost barriers.
With the Bundle, if you already have production-grade RPC and gRPC connections, you can add Shredstream for a lower combined price. The pack pricing removes psychological barriers to adoption.
First, build your base app quickly with RPC + gRPC, then learn Shredstream and transition to higher performance within the same environment. Power users ingest both processed and confirmed data directly via Shredstream alone, which requires custom client development. The Bundle provides a reliable path to receive Shredstream, serving as a bridge to that advanced step.
The Bundle’s gRPC has no filter restrictions, and during product development it also supports RPC on Devnet and Testnet.
It is an ideal way to start Solana development and move smoothly into production.
For adoption or migration, contact Validators DAO Official Discord.
- Validators DAO Official Discord: https://discord.gg/C7ZQSrCkYR
Premium Ryzen VPS
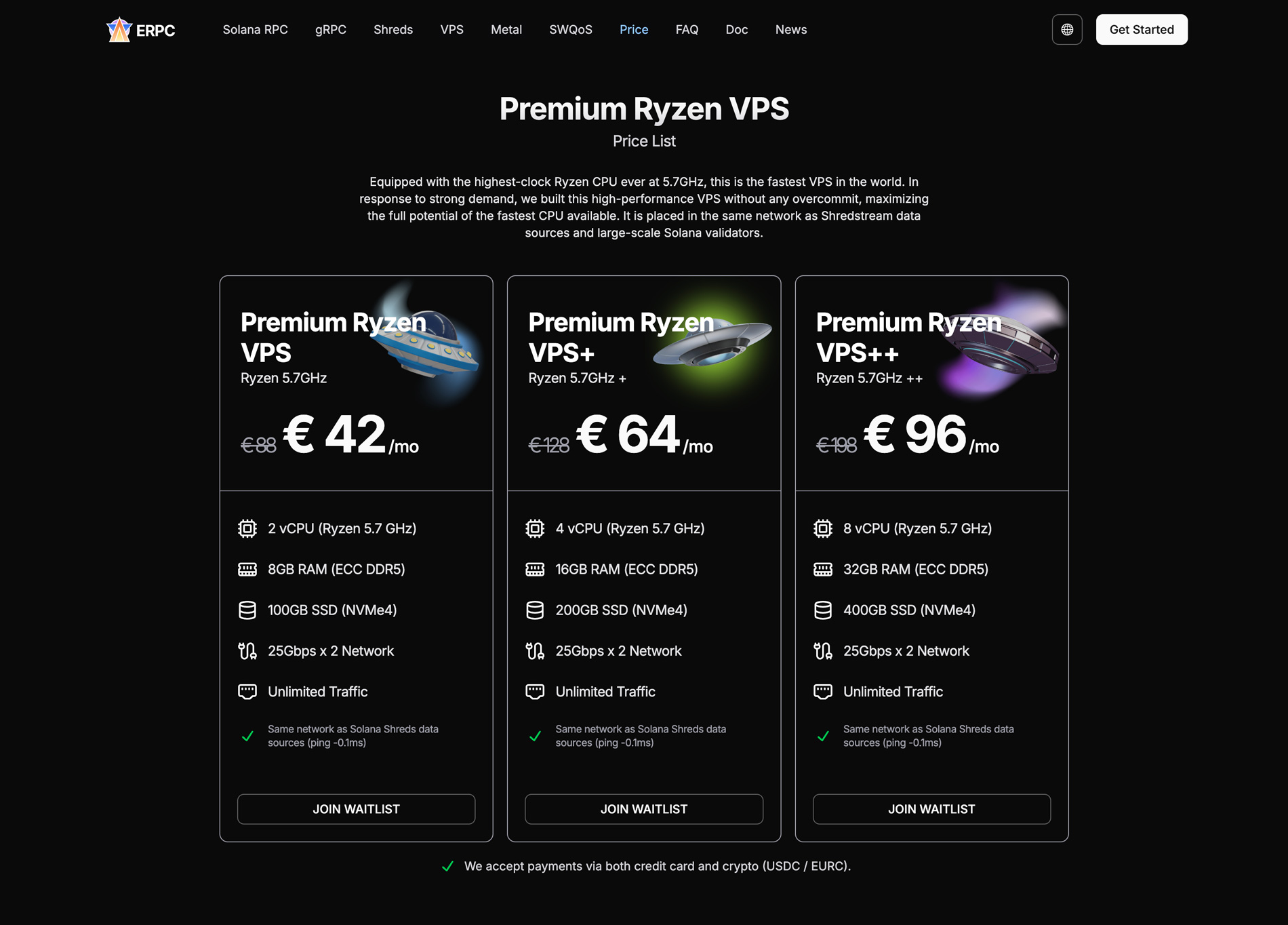
Premium Ryzen VPS runs on the same network as ERPC. It features world-class 5.7 GHz high-clock CPUs, ECC DDR5 memory, NVMe4 storage, and dual 25 Gbps networking. With zero overcommit, it delivers bare-metal class stability despite being virtualized.
It is colocated in the same data centers as major Solana validators and Jito Shredstream. Zero-distance connectivity removes internet latency. This configuration balances performance and cost efficiency and is highly regarded by many projects.
- Validators DAO Official Discord: https://discord.gg/C7ZQSrCkYR
Problems ERPC and Validators DAO solve
- Transaction failures and latency fluctuation common in general-purpose RPC environments
- Performance limits imposed by many infrastructure providers
- The significant impact of network distance on communication quality
- The difficulty small projects face in accessing high-quality infrastructure
While developing the open-source Solana NFT card game Epics DAO, we faced the challenge that high-quality, high-speed Solana development environments were not easy to obtain. We built our own platform and now provide ERPC and SLV based on that experience.
Financial applications are especially mission critical, and latency or errors directly affect user experience. With distributed validators and Web3-specific structures overlapping, it is hard to grasp the whole, and many projects have struggled with delay and instability.
We provide the high-performance foundation that teams need and contribute to better developer and user experience across the Solana ecosystem. ERPC and SLV are part of this effort.
- ERPC Official Site: https://erpc.global/en
- SLV Official Site: https://slv.dev/en
- Epics DAO Official Site: https://epics.dev/en
- Validators DAO Official Discord: https://discord.gg/C7ZQSrCkYR